Hearing & Audiology
 Hearing Loss in the Dental Profession
Hearing Loss in the Dental Profession
Occupational noise-induced hearing loss is estimated to be the most common occupational disability in the United States. Although noise exposure in the dental office is typically intermittent, dental professionals have been shown to be at risk of hearing loss, as the noise generated by some dental equipment can approach established exposure limits. In addition to hearing loss, high noise levels caused by some dental equipment can create stress, and can interfere with a dental professional’s communication and concentration. Wearing hearing protection devices (HPDs) is one way that dental professionals can reduce the harmful effects of office noise.
Dentists and dental staff are exposed to the noise of handpieces and ultrasonic scalers, at levels of 60-99 decibels. While this level of noise presents only a minimal risk of hearing loss, sustained exposure can result in sensorineural hearing loss. Just as you tell your patients to brush and floss to prevent oral diseases, you can practice what you preach and adopt some preventive measures to preserve your hearing.
Learn to recognize the symptoms and causes of this workplace hazard. Follow the easy and prudent tips to prevent hearing loss before it has even started.
Tips for Preventing Noise-Induced Hearing Loss- When using dental equipment, wear ear plugs or noise-cancelling (over-the- ear) headphones. The ADA Professional Product Review has data to help with selecting hearing protective devices (HPD).
- In selecting dental equipment, consider its noise level as a factor in your purchasing decision
- Have your hearing tested to establish a baseline of the status
- Monitor your hearing acuity on a regular basis to have any problems correctly diagnosed and to benefit from early intervention.
What’s Too Loud?Hearing protection is needed when the sound a person is exposed to is over 85 decibels. Sounds that are over this threshold include:
- Busy street: 75-85 dB
- Lawn mower: 85 dB
- *** Dental Equipment: 66-99 dB ***
- Car horn: 110 dB
- Chainsaw: 115-120 dB
- Rock concert or ambulance siren: 120 dB
Types of Hearing Protection There are three main types of hearing protection that people can wear to help reduce the impact of noisy environment and risk of developing noise-induced hearing loss.
- Earplugs
- Earmuffs/Noise canceling Earphones
- Semi-insert Earplugs
Earplugs are premolded/preformed or moldable foam plugs that can be inserted into the ear canal. They are available as disposable or reusable and can be found in most drug stores and grocery stores.
Semi-insert custom-molded earplugs are available and can be made by visiting your audiologist or other hearing healthcare professional
. Earmuffs are made with sound-attenuating material and soft ear cushions that fit around the hard-outer cups. They are held together with a headband. They are quite adept at muffling sound out, protecting people from over exposure to loud noises
. Noise canceling headphones can cancel out unwanted noise and are made by many name brand companies.
Diagnosing Hearing Loss- Hearing Screening:
- Hearing screening is a test to tell if people might have hearing loss. Hearing screening is easy and not painful. It takes a very short time — usually only a few minutes.
- Full Hearing Test:
- An audiologist, who is an expert trained to test hearing, will do the full hearing test. In addition, the audiologist will also ask questions about birth history, ear infection and hearing loss in the family. There are many kinds of tests an audiologist can do to find out if a person has a hearing loss, how much of a hearing loss there is, and what type it is. The hearing tests are easy and not painful.
Hearing Aids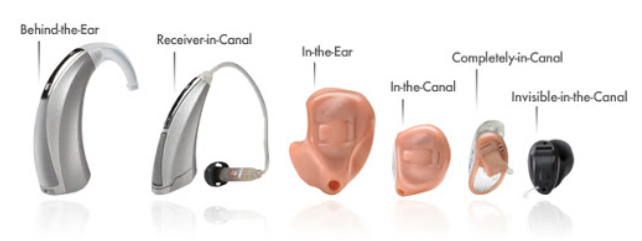
The best hearing aid for you is one the that you feel comfortable wearing and that fits your lifestyle. Today, there are hundreds of hearing aids on the market that are comfortable, nearly invisible and offer high fidelity sound quality. There are even extended wear hearing aids you leave in for months, and hearing aids that wirelessly connect to your TV through your smartphone, transforming your hearing aids into headsets.
Styles of hearing aids include traditional behind the ear and mini behind the ear, receiver in the ear and receiver in the canal. Each brand offers several different styles and technological advancements.
Which hearing aid is right for you? A professional audiologist will help you choose hearing aids that match the environments where you spend time, your lifestyle and your budget. They will adjust and program your hearing aids for the best hearing possible. The right hearing aids can transform your life.
** The above content was taken from "Safety/Ergo Tips: Hearing Loss". developed through OSHA’s Alliance Program as a product of the OSHA and ADA Science and Research Alliance. It’s intended for informational purposes only and does not endorse any specific company or brand.
Hearing Loss & Tinnitus- Tinnitus is described as the regular presence of buzzing, ringing, or rattling sounds, even when there is no external source causing these sounds to occur.
- Dentists are 50% more likely to suffer from tinnitus and hearing loss compared to the general population.
- Approximately 50 million Americans experience tinnitus, 90% of which also report having hearing loss.
 Hearing Loss in the Dental Profession
Hearing Loss in the Dental Profession